Information Technology (IT) and industrial equipment and automation networks (IoT, Operations Technology) are connected through the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) (IT). Cloud, mobile, and edge computing are redefining IT. It enables customers to use IIoT applications for predictive quality and maintenance and monitor their operations everywhere remotely.
The value of IIoT can be challenging to realize, and there are usually the following three factors that are holding manufacturers back:
- Data collection is frugal and infrequent
- Difficulty in data accessibility
- Limited scope to link data silos
Current situation and challenges of the Industry
PLCs or large Distributed Control Systems (DCS) with real-time distributed control networks (Fieldbus) connecting them, and Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems are among the operational technologies that many industrial companies have invested heavily in. It is complicated to replace active technologies designed and deployed to last a couple of decades.
As a result, we must adapt existing equipment and systems, which were not designed for IoT applications. For smooth adaptation, we need to overcome the below hurdles.
- We need to collect data from devices (sensors, actuators, electrical motors) made by different companies. Most of the time, our systems are retrofitted with new technology to measure, allow remote control and communicate.
- Along with connectivity, security is the second and most significant challenge to overcome. The device and its data must be kept secure. When a piece of equipment or system fails in a production environment, the downtime and business impact can be severe. Without cloud connectivity, we need to ensure that industrial connected devices can perform at their peak performance. Device operation must not be affected by data collection processes. Any remote control or update must be performed securely by only authorized operators.
- Insights come as a third challenge once the data is secure. Whether the data comes from different devices or manufacturers or fieldbuses?, systems, or databases, it’s crucial to link the data together.
How it works
IoT helps industrial companies overcome challenges to attain business goals.
- IoT allows you to connect, manage, and update devices of any type with ease, from tiny microcontrollers to more powerful gateway devices. Simple sensors can monitor processes and track key performance indicators without overhauling or replacing existing hardware on the manufacturing floor, such as Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC) and Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems.
- Device authentication and authorization are built-in to IoT, so your data and devices are kept secure. Monitoring your device fleet for abnormal behavior and receiving alerts if something doesn’t look right are other features available. Some devices can be powered off, or a security update can be downloaded.
- A third benefit of the Internet of Things (IoT) is that connected devices can operate with intermittent Internet connectivity, thereby reducing the risk of unplanned outages. If you don’t have access to the Internet, you can run machine learning models or software code locally and store data until you can connect.
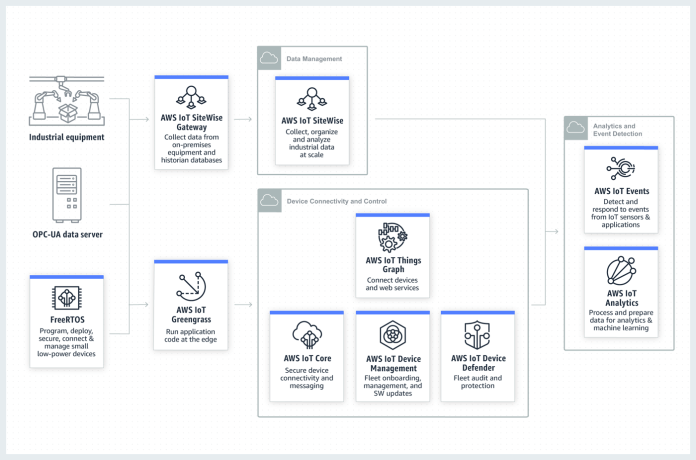
Why should any enterprise go through this hurdle to enable end-to-end IoT
It is possible to scale your IoT applications to thousands or millions of devices using platforms like AWS and Azure. These IoT platforms allow you to monitor your devices and update device software over the air (OTA).
IoT offers an easy way to run analytics on IoT data once devices have been securely installed. As a result, you can gain operational insights from IoT data. It is possible to build machine learning models for your industrial IoT data by integrating IoT with platforms. In addition to running in the cloud, these models can also be installed locally on devices. You can visualize and explore data, and you can share insights with other members of your team and other departments.
IoT platforms allow connected devices to quickly and securely communicate with cloud-enabled applications and other IoT-enabled devices as a managed cloud service. In addition, the platform can process and route messages reliably and securely to endpoints, as well as other devices. Following the business rules you set up, it can filter, transform, and act on device data quickly. The use of IoT Rules by companies can allow for the automatic detection of real-time data and routing this information to the appropriate service. It is also a part of IoT Analytics, which is integrated with the platform, where machine learning can be used to analyze the data. Data from other sources can be added to IoT data from equipment/devices, gaps can be filled if data is missing, false readings can be eliminated, and mathematical operations can be performed if sensors are not calibrated correctly.
A detailed explanation of how the IoT Services support the most important industrial use cases is given below:
- Asset Condition Monitoring
- Predictive Maintenance
- Predictive Quality
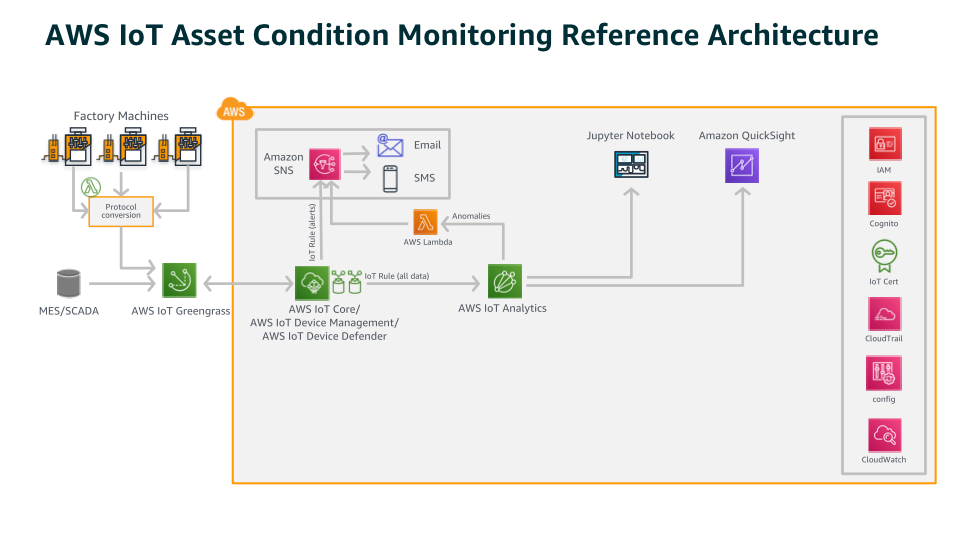
Asset Condition Monitoring
As a result of asset condition monitoring, you can understand how your machines and equipment performance in the field or on the factory floor. Since technicians need to inspect machines physically, it’s difficult to manually collect data such as temperature, vibration, and error codes. Your organization can capture and monitor IoT data with the help of the IoT platform. Your assets will be better utilized, and your investment will be fully rewarded.
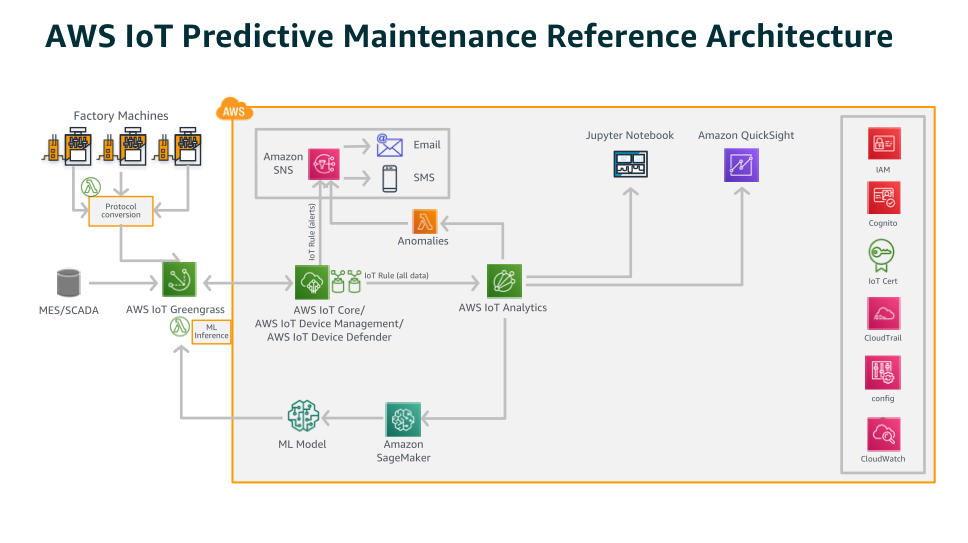
Predictive Maintenance
As a result, you can identify potential breakdowns before they harm production. Equipment health and performance can be continually monitored with IoT, allowing for real-time detection of faults. Equipment lasts longer, worker safety is improved, and the supply chain is optimized when organizations use predictive maintenance analytics.
Predictive Quality
Predictive quality analytics extract actionable insights from industrial data sources such as manufacturing equipment, environmental conditions, and human observations. Its goal is to identify actions, such as adjusting machine settings or using different sources of raw materials, that will improve the quality of factory output. Industry can build predictive quality models using IoT. Customers are more satisfied with higher-quality products, and product recalls are reduced.
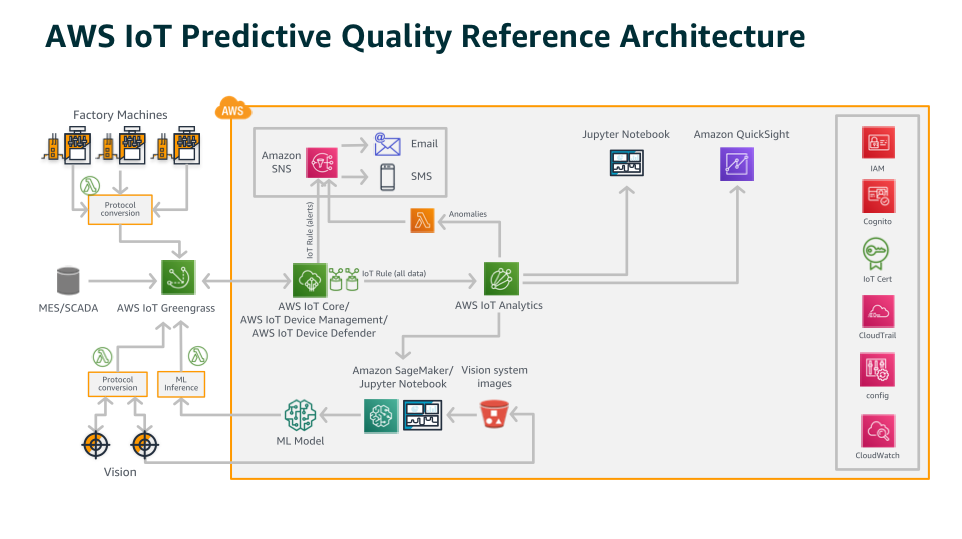
The onboarding of legacy equipment is often a concern for industrial companies when they begin building IoT applications. Data and device security, unplanned downtime, and gaining valuable insights from collected data are some of the issues that need to be addressed in the future. AWS and Azure IoT partners can provide “plug and play” capabilities to connect with existing equipment, no matter what manufacturer, extract data from devices, and securely control them. IoT has the power to unlock new revenue models from existing or sleeping products and processes, which is why it is celebrated by business leaders all over the world.